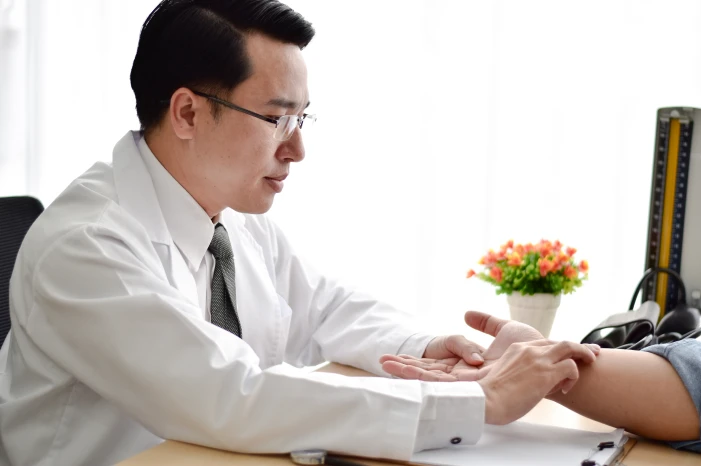
Method
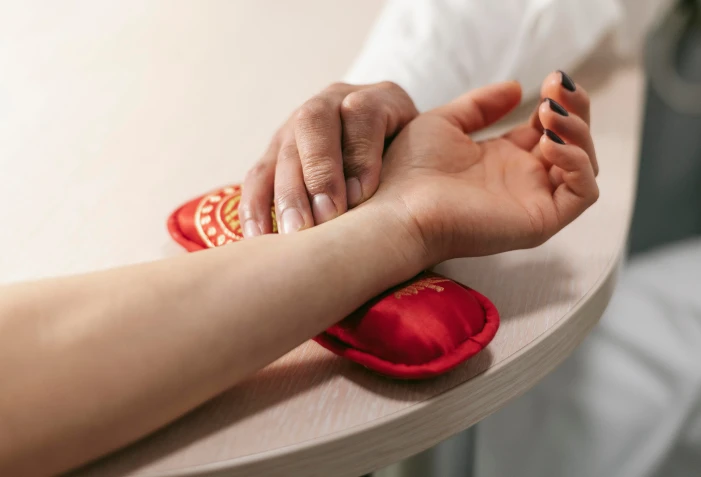
The blood circulating in the human body carries information about the state of the internal organs and their systems. An experienced doctor knows how to decipher this information. By examining the location, frequency and nature of the pulse, the doctor can determine the location of the disease, its nature and severity, as well as possible consequences.
Pulse as an indicator of health in Chinese medicine
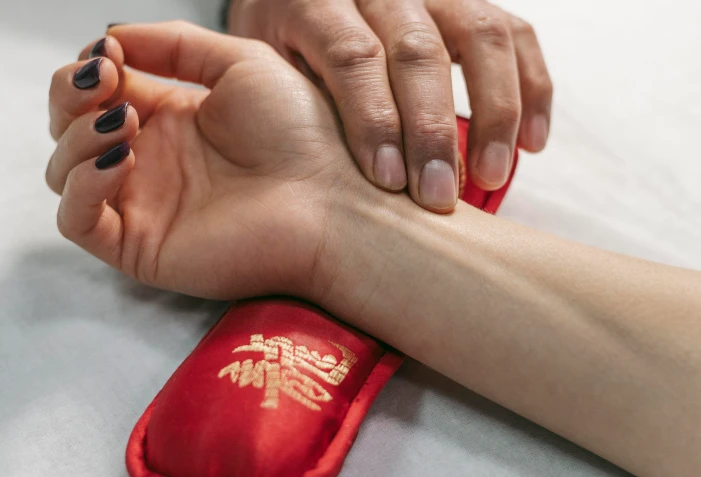
The pulse of a healthy person is from 70 to 80 beats per minute, in a child - 110 beats per minute. Any deviations from these parameters indicate various disorders in the functioning of the body. Chinese medicine distinguishes about 30 types of pulse, each of which is often more informative than laboratory tests and expensive diagnostic studies.



Make an Appointment
Make an appointment at the medical center "Sad Dolgoletia" and trust our professionals to take care of your health. A comprehensive approach, modern treatment methods and individual attention to each patient!
Traditional methods of diagnostics by pulse
In the ancient Chinese tradition, there were various options for pulse diagnostics, which were carried out on different parts of the body. The most popular and accurate is considered to be reading the pulse at six points on the wrists of both hands.
Additionally, the pulse is divided into levels: superficial, medium and deep. They can be used to find out about the health of all important organs. According to Chinese tradition, on the left hand the deep level corresponds to: the heart, liver and left kidney, on the right: the lungs, spleen and right kidney. These are the so-called "dense" organs.
Comprehensive approach to diagnostics in Chinese medicine

At the superficial level of the pulse, pathologies are recognized in the group of "hollow" organs. On the left hand: the small intestine, gall bladder and urinary bladder. On the right hand: the large intestine, stomach and the so-called "triple heater" - a conventional organ in traditional Chinese medicine that controls the transformation of the vital energy Qi in the human body.
Pulse diagnostics are most often carried out in combination with other traditional diagnostic methods, such as examination and diagnostics by tongue. Only with a systemic analysis of the patient's condition can one obtain the most complete picture of his diseases.



